유텍 환원 코엔자임 Q10은 소비자의 보다 효율적인 영양 요구 충족을 지원하기 위해 SCI 저널 "제약"에 등재되었습니다.
하이드록시티로솔 공결정 기술이 권위 있는 학술지에 발표된 데 이어, 또 다른 차세대 환원제인 코엔자임 Q10 메이 쉬에펑 교수와 그의 연구팀이 공결정 기술을 이용해 만든 유비퀴놀은 성공적으로 출시되었으며, 연구 결과는 최근 SCI 저널 '제약'에 '유비퀴놀의 공결정: 안정성 및 생체이용률 향상'이라는 제목으로 게재되었습니다.
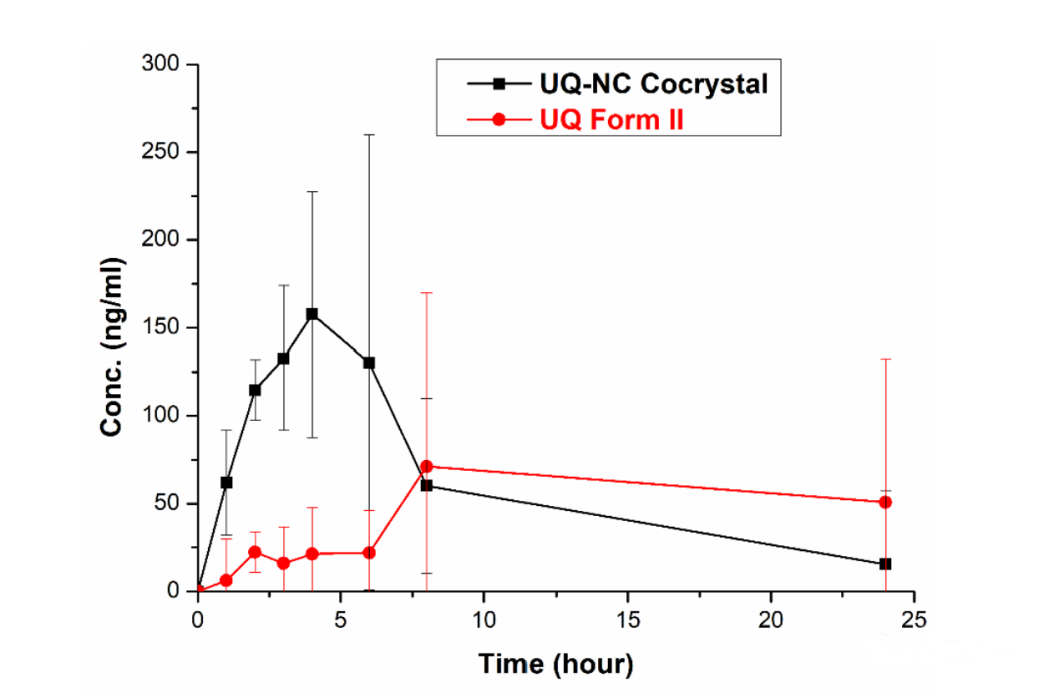
이 글에서는 주로 새로운 환원 코엔자임 Q10과 비타민 B3 니코틴아마이드 공결정(UQ-NC)을 합성하기 위해 팀 전체가 공결정 기술을 사용하는 방법을 소개합니다. 그리고 이 유텍틱 제품을 시중에서 판매되는 제품과 비교해 보세요. 대조적으로, 공동 결정은 코엔자임 Q10 은 안정성이 뛰어나고 용해성이 좋으며 생체 이용률이 높습니다. 가속 조건에서 6개월 동안 보관한 후에도 유텍틱 환원 코엔자임 Q10의 함량은 기본적으로 변하지 않았습니다. 용해도 실험 결과, 시뮬레이션 위액에서 코큐텐의 최대 용해 농도는 시판 원료의 12.6배, 시뮬레이션 장액에서 시판 제품의 38.3배에 달했습니다. 동시에 쥐를 대상으로 공결정 환원 코엔자임 Q10과 시판 코엔자임 QH의 생체 이용률을 비교했습니다. 그 결과 공결정의 최대 혈중 농도는 시판 제품의 2.2배, AUC는 시판 제품의 4.5배에 달하는 것으로 나타났습니다.

미토콘드리아 전자 수송 사슬의 중요한 구성 요소 중 하나인 세포 내 코엔자임 Q10은 세포의 미토콘드리아에서 아데노신 삼인산(ATP)의 합성을 촉진하여 세포에 에너지를 공급합니다. 심근 세포는 인체에서 에너지를 가장 많이 소비하는 세포 중 하나이므로 다른 장기에 비해 심장은 코엔자임 Q10에 대한 의존도가 매우 높습니다. 실험에 따르면 코엔자임 Q10은 심근 세포의 에너지 합성 효율을 개선하고 심근 세포의 신진 대사 수준을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 따라서 심근 세포에서 코엔자임 Q10의 함량을 증가시킴으로써 미토콘드리아의 작업 추진력을 유지하고 개선 할 수 있으며 세포 내 영양소의 에너지 전환 능력을 향상시킬 수 있으며 심장에 공급하기에 충분한 ATP 에너지를 생성 할 수 있으며 심장의 에너지 공급을 개선 할 수 있습니다. 젊을 때는 균형 잡힌 식단을 통해 충분한 코큐텐을 섭취할 수 있습니다. 나이가 들어감에 따라 적절한 양의 외인성 코큐텐 보충제를 섭취하면 인체 세포의 코큐텐 부족을 보충하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
코엔자임 Q10 은 환원된 형태(유비퀴놀)와 산화된 형태(유비퀴논)의 두 가지 형태로 존재합니다. 이 두 가지 형태는 서로 전환될 수 있지만, 산화 코엔자임 Q10은 세포에서 직접 활용할 수 없으며 생물학적 기능을 발휘하려면 환원 코엔자임 Q10(코엔자임 QH)으로 전환되어야 합니다. 그러나 환원 코엔자임 Q10(코엔자임 QH)은 안정성이 떨어지고 쉽게 산화됩니다. 실온에서 한 달 안에 70% 이상 분해될 수 있습니다.
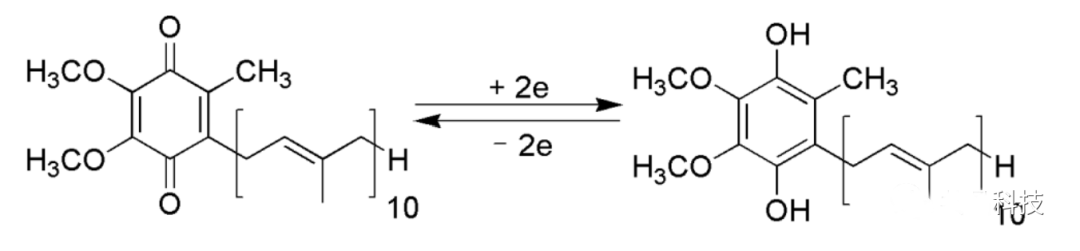
공결정 기술로 제조된 차세대 환원 코엔자임 Q10(코엔자임 QH)은 환원 코엔자임 Q10의 불안정한 문제점을 해결하고 생체이용률을 개선하여 보다 풍부한 제형을 개발할 수 있는 가능성을 제시했습니다. 이를 통해 소비자들의 보다 정확하고 효율적인 영양 요구를 충족시킬 수 있는 기반을 마련했습니다.
() ()


