Cosmetic raw material with whitening effect——Arbutin

무엇 알부틴
알부틴이라고도 알려진 알부틴은 화학명은 4-하이드록시페닐-D-글루코피라노사이드이며 상대 분자량은 272.25입니다. 녹색 식물에서 추출한 자연 발생 배당체이며 진달래과의 밀, 배, 베어베리 등 내성이 강한 동결 건조 식물에 많이 함유된 성분으로 용질이 풍부합니다. 흰색 바늘 모양의 결정 또는 분말 형태로 나타납니다. 뜨거운 물, 메탄올, 에탄올, 프로필렌글리콜, 글리세린에 쉽게 용해되며 에테르, 클로로포름, 석유에는 불용성입니다. 에테르와 같은 용매.
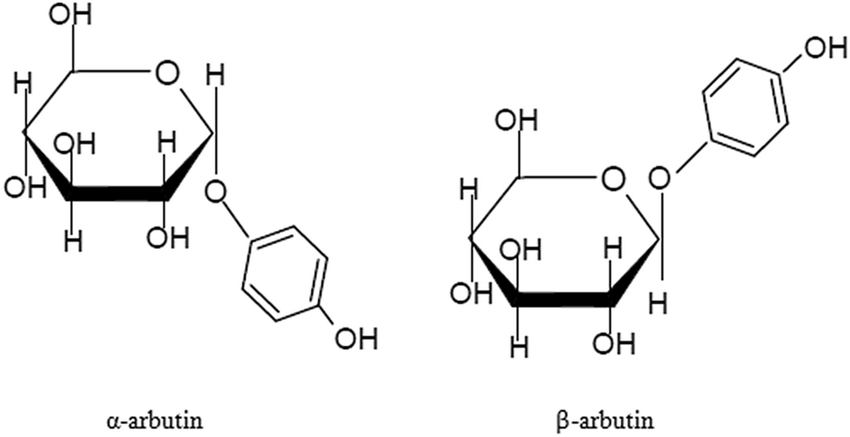
알부틴 can be divided into α-type and β-type according to different structures. The chemical name of α-arbutin is 4-hydroxyphenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside, and the chemical name of β-arbutin is 4-hydroxyphenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside. α-Arbutin is the epimer of β-arbutin, and the direction of its glycosidic bond in space is opposite to that of β-arbutin (see figure for details)
The whitening mechanism of arbutin
멜라닌의 함량과 분포는 피부색의 깊이를 결정하는 주요 요인입니다. 멜라닌은 피부 표피의 기저층에 있는 멜라닌 세포에서 생성됩니다. 일련의 복잡한 생화학 반응을 통해 티로시나아제의 작용으로 티로신에서 최종적으로 형성됩니다. 시냅스를 통해 안쪽에서 바깥쪽으로 표피의 기저층에서 바깥층으로 전달됩니다. 피부에 색을 입히세요.
티로시나아제는 티로신 하이드 록실 라제 활성 (티로신을 촉매하여 도파 생성)과 도파 산화 효소 활성 (도파를 촉매하여 도파퀴논 생성)을 가지고 있습니다. 멜라닌 형성 과정에서 주요 속도 제한 효소 역할을 합니다. 이 효소의 활성에 따라 형성되는 멜라닌의 양이 결정됩니다.
알부틴은 세포 증식 농도에 영향을 주지 않고 티로시나아제 활성을 효과적으로 억제할 수 있는 티로시나아제 억제제입니다. 티로시나아제에 직접 결합하여 도파의 결합을 경쟁합니다. 부위에 결합하여 도파와 도파퀴논의 합성을 차단하여 멜라닌 세포를 방해하고 멜라닌 생성을 억제합니다. 동시에 형성된 멜라닌을 희석하고 멜라닌의 분해와 배설을 촉진하며 피부 색소 침착을 줄이고 기미와 주근깨를 제거하는 기능도 있습니다.
Preparation method of 알부틴
natural plant extraction method
This method mainly uses plant leaves of the genus Ursi as raw materials, and uses organic solvent extraction, extraction, column chromatography and other separation and purification methods to obtain arbutin extract. As early as 1930, it was reported that arbutin is contained in the leaves of rock cabbage. Subsequent studies have confirmed that arbutin is also found in the leaves of black rice tree, bilberry, bearberry and pear tree. glycosides.
Since the content of arbutin in plants is very low, the extraction process is relatively complex, and the purity of the extract is not high, so with the development of other preparation methods, the plant extraction method has gradually lost its competitive advantage.
plant tissue culture
The plant tissue culture method utilizes the glycosylation ability of plant cells to convert hydroquinone into arbutin. Compared with plant extraction methods, the efficiency of obtaining arbutin using plant tissue culture methods is much higher. When applying this method, selecting an efficient plant tissue culture medium and determining appropriate culture conditions are key.
The raw materials used in the plant tissue culture method are clean, the conversion rate is high, and the production is pollution-free. However, the production cycle is long, the separation and purification is complicated, and the industrial development is relatively immature. Further understanding the growth mechanism of plant cells, clarifying the key influencing factors of the synthesis process, shortening the production cycle, and improving yield are the key issues that need to be solved in the application of this method.
enzyme synthesis method
The enzyme synthesis method mainly uses glycosyltransferase or glycosidase as a catalyst to catalyze glycosyl transfer and reverse hydrolysis reactions to synthesize glycosides, that is, arbutin is obtained from hydroquinone and glucose under the catalysis of glycosidase.
The enzyme synthesis method has a simple process, high synthesis efficiency, and very optimistic development prospects. With in-depth research on this method in recent years, more and more suitable zymogens have been discovered, and the synthesis rate of arbutin is also getting higher and higher. It is believed that this method will be one of the main research directions for the synthesis of arbutin in the future. one.
chemical synthesis
Generally, chemical synthesis of arbutin uses glucose and hydroquinone as raw materials. After the two are appropriately protected, they undergo a glycosidation reaction and then remove the protecting group. The chemical synthesis method has become the most important method for preparing arbutin due to its advantages of better synthetic product quality and lower production cost, and has achieved industrial production at home and abroad.
At present, in China, anhydrous glucose is generally used as raw material, and β-arbutin is produced through acylation protection, catalytic condensation, and alkaline hydrolysis. With the continuous development of synthesis technology, in recent years, the steps for domestic synthesis of arbutin have been gradually simplified, the synthesis rate has been continuously improved, and the quality has reached the international advanced level. However, due to the poor stereoselectivity of the product in chemical synthesis, more in-depth research is still needed to find an efficient and specific chemical synthesis method for preparing α-arbutin.
() ()