Ethereum: Bitcoin Block Size – What are the rules?
Ethereum: Understanding of block size rules
When it comes to scaling and performance, one of the most critical factors in the Ethereum network is the size of the block. The size limit of the block refers to the maximum number of bytes that can be stored in an Ethereum block. In this article, we will deepen the rules that regulate the size policy of the Ethereum block.
What is a block size?
A size of the block refers to the total amount of space occupied by all transactions and data stored in an Ethereum block. Think about it as a digital container that has several transactions, such as transactions, data packages and other types of content. Each transaction has a unique identifier called “transaction ID”, which is used to identify the sender, recipient and type of transaction.
Maximum block size
The maximum limit of the Ethereum block was set at 2 Gigabyte (GB) by the Ethereum Foundation in April 2017. This means that an individual block cannot exceed this limit, even if it contains more transactions or data packages. If a block is too high, it can cause problems with the network performance and reliability.
The minimum size of the block
The minimum size of the block is not explicitly defined in the Ethereum protocol, but it has been estimated to be around 1-2 megabyte (MB) based on different analyzes and simulations. This means that, even if a block contains very few transactions or not given at all, a certain block space would be needed.
Can I have a block with 0 transactions included?
Yes, you can have a block with 0 transactions included. In fact, this is possible because the Ethereum protocol allows the blocks to be empty of content. This is done using a special type of transaction called a “transaction fee” to pay the calculation power needed to create and validate the block.
Why is the size of the block important?
The size of the block affects several aspects of an Ethereum network:
- Transaction processing : Larger blocks can handle more transactions in less time, improving the general network performance.
- Network scalability
: As the network increases, larger blocks increase scalability, allowing more users and applications to participate.
- セキュリティ : The smaller dimensions of the block can be more vulnerable to attacks, as they offer opportunities for bad actors to manipulate or manipulate data in a block.
結論
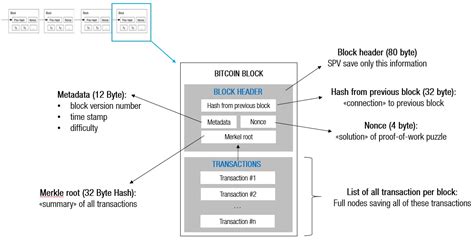
The size policy of the Ethereum block is an essential aspect of network architecture and performance. Understanding the maximum and minimum limits of the size of the block helps users and developers plan their applications and transactions accordingly. While you can have a block with 0 transactions included, it is crucial to consider the implications for processing transactions, network scalability and security.
参考文献
- Ethereum Foundation. (2017). “Ethereum 1.0: the first block”.
- Ethereum Foundation. (2022). “Ethereum Smart Contract Language”.
Note: This article is a general overall image of the Ethereum block size rules. For specific protocol information, please see WhitePaper Ethereum or Official Documentation.
