Cosmetic raw material with whitening effect——Arbutin

何なのか? アルブチン
アルブチンはアルブチンとしても知られ、化学名 は4-ヒドロキシフェニル-D-グルコピラノシド、相対分子 量は272.25である。緑色植物に由来する天然由来の配糖体であり、多くの耐性植物の成分である。小麦、梨、シャクナゲ科のクマノミなどのフリーズドライ植物には、溶質が豊富に含まれている。それらは白い針状の結晶や粉末として現れる。熱水、メタノール、エタノール、プロピレングリコール、グリセリンに溶けやすく、エーテル、クロロホルム、石油には溶けない。エーテルなどの溶媒。
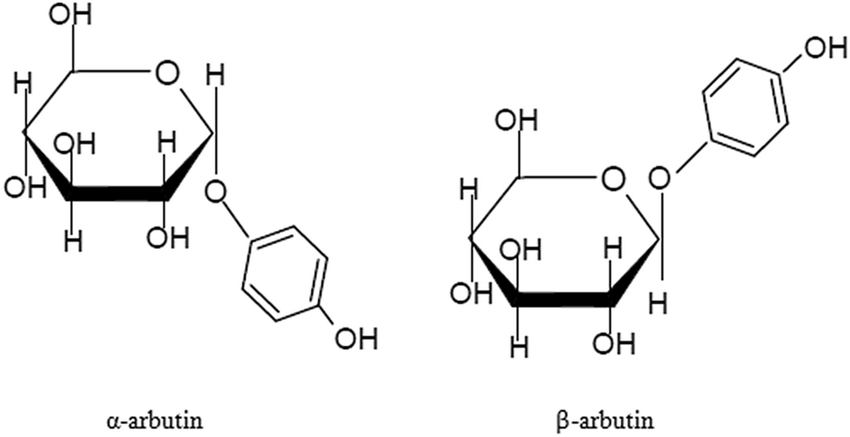
アルブチン can be divided into α-type and β-type according to different structures. The chemical name of α-arbutin is 4-hydroxyphenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside, and the chemical name of β-arbutin is 4-hydroxyphenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside. α-Arbutin is the epimer of β-arbutin, and the direction of its glycosidic bond in space is opposite to that of β-arbutin (see figure for details)
The whitening mechanism of arbutin
メラニンの含有量と分布が、肌の色の濃さを決める主な要因である。メラニンは、皮膚表皮の基底層にあるメラノサイトで生成される。チロシナーゼの作用により、一連の複雑な生化学反応を経て、最終的にチロシンから生成される。シナプスを介して基底層から表皮の外側に内側から伝達される。皮膚に色をつける。
チロシナーゼは、チロシンヒドロキシラーゼ活性(チロシンを触媒してドーパを生成する)とドーパオキシダーゼ活性(ドーパを触媒してドーパキノンを生成する)を持つ。メラニン生成の過程では、この酵素が主要な律速酵素の役割を果たす。その活性は、形成されるメラニンの量を決定する。
アルブチンは、細胞増殖濃度に影響を与えることなく、チロシナーゼ活性を効果的に阻害することができるチロシナーゼ阻害剤である。チロシナーゼに直接結合することでドーパの結合を競合させ、ドーパとドーパキノンの合成を阻害することで、メラノサイトを妨害し、メラニンの生成を抑制する。同時に、形成されたメラニンを薄め、メラニンの分解・排泄を促進し、皮膚の色素沈着を抑え、シミ・ソバカスを除去する作用もある。
Preparation method of アルブチン
natural plant extraction method
This method mainly uses plant leaves of the genus Ursi as raw materials, and uses organic solvent extraction, extraction, column chromatography and other separation and purification methods to obtain arbutin extract. As early as 1930, it was reported that arbutin is contained in the leaves of rock cabbage. Subsequent studies have confirmed that arbutin is also found in the leaves of black rice tree, bilberry, bearberry and pear tree. glycosides.
Since the content of arbutin in plants is very low, the extraction process is relatively complex, and the purity of the extract is not high, so with the development of other preparation methods, the plant extraction method has gradually lost its competitive advantage.
plant tissue culture
The plant tissue culture method utilizes the glycosylation ability of plant cells to convert hydroquinone into arbutin. Compared with plant extraction methods, the efficiency of obtaining arbutin using plant tissue culture methods is much higher. When applying this method, selecting an efficient plant tissue culture medium and determining appropriate culture conditions are key.
The raw materials used in the plant tissue culture method are clean, the conversion rate is high, and the production is pollution-free. However, the production cycle is long, the separation and purification is complicated, and the industrial development is relatively immature. Further understanding the growth mechanism of plant cells, clarifying the key influencing factors of the synthesis process, shortening the production cycle, and improving yield are the key issues that need to be solved in the application of this method.
enzyme synthesis method
The enzyme synthesis method mainly uses glycosyltransferase or glycosidase as a catalyst to catalyze glycosyl transfer and reverse hydrolysis reactions to synthesize glycosides, that is, arbutin is obtained from hydroquinone and glucose under the catalysis of glycosidase.
The enzyme synthesis method has a simple process, high synthesis efficiency, and very optimistic development prospects. With in-depth research on this method in recent years, more and more suitable zymogens have been discovered, and the synthesis rate of arbutin is also getting higher and higher. It is believed that this method will be one of the main research directions for the synthesis of arbutin in the future. one.
chemical synthesis
Generally, chemical synthesis of arbutin uses glucose and hydroquinone as raw materials. After the two are appropriately protected, they undergo a glycosidation reaction and then remove the protecting group. The chemical synthesis method has become the most important method for preparing arbutin due to its advantages of better synthetic product quality and lower production cost, and has achieved industrial production at home and abroad.
At present, in China, anhydrous glucose is generally used as raw material, and β-arbutin is produced through acylation protection, catalytic condensation, and alkaline hydrolysis. With the continuous development of synthesis technology, in recent years, the steps for domestic synthesis of arbutin have been gradually simplified, the synthesis rate has been continuously improved, and the quality has reached the international advanced level. However, due to the poor stereoselectivity of the product in chemical synthesis, more in-depth research is still needed to find an efficient and specific chemical synthesis method for preparing α-arbutin.
() ()