Ethereum: How do zkSync Blocks Work?
Understanding Blocks Zksync: Deep Fixing in Lateral Ethereum
When you deepen more in the ZK-Sync world, the consensual mechanism in this article, we decompose what the L1 Lots Ethereum and its century are.
What is zksync block?
The ZK synchronization block applies to one block of blockchain containing multiple transactions. In the context of Sidececains, each part of the L1 represents a collection of transactions that are carried out in the side market network. Each transaction is encoded as a separate Merkle branch or a series of hash values that collect a collective block.
Many L1 vs. Blocks of tread
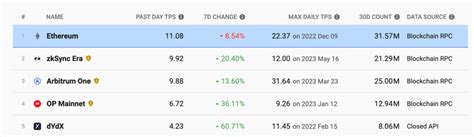
While both expressions describe transactions collections in one block, they differ in their basic architecture:
* L1 L1 : These are the individual components that make a lot of L1. They contain several coded transactions such as separate Merkle branches or hash values.
* Launch blocks : Instead, the rolling blocks are many transactions combined in one block. Every transaction in the plot is merged with others to create a new block.
How do the Zksync blocks work?
When sending L1, a lot to Ethereum as LOT L1 are basically replicated in the Ethereum network and then joined to the treadmill. Here is a step by step to divide how this process works:
1.
- Get rid of : When the replication process is completed, the L1 parts are chained in one cylindrical block.
3
Example
Suppose you send five L1 of land (each containing three transactions) to Ethereum as LOT L1. The resulting cylinder block would contain five separate blocks, each of which has its own transactions:
Block 1: Transaction 1
Rollup Block 2: Transaction 2
Rollup Block 3: Transaction 3
Block 4: Transaction 4
Block 5: Transaction 5
In this scenario, each part of the L1 is replicated on the Ethereum and then connected to the running belt, leading to a brief final block containing all five individual plots.
Conclusion
ZK-synchronization blocks play an important role in allowing safe interactions between Ethereum and its side plans. Understanding how these mechanisms work can be designed by developers more efficient and scalable applications for their use. Whether you build a decentralized financial protocol (Defi) or identity management system, it is necessary to understand the complexity of Sync ZK blocks for the success of the Ethereum network.
Following this guide, you will get a deeper understanding of how L1 LOTS works in the context of ZK-Sync, and you will be better equipped to solve complex problems in the world of decentralized applications.
