¿Por qué se llama a la astaxantina "limpiadora de vasos sanguíneos"? ¿Qué tiene de mágico?

Why can astaxantina clean up blood vessels? Astaxanthin’s powerful wall-breaking ability makes it the only carotenoid that can penetrate the “blood-brain barrier”.
The inner wall of healthy blood vessels is smooth and dense, and blood flows smoothly. However, the inner wall of blood vessels after atherosclerosis becomes rough and is easily adhered to by nutrients such as fat and sugar. Astaxanthin’s powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties allow it to repair damaged mucosal barriers of blood vessels, restoring the blood vessel walls to a smooth and dense state, making it impossible for nutrients to cling to them, and preventing secondary recurrences.
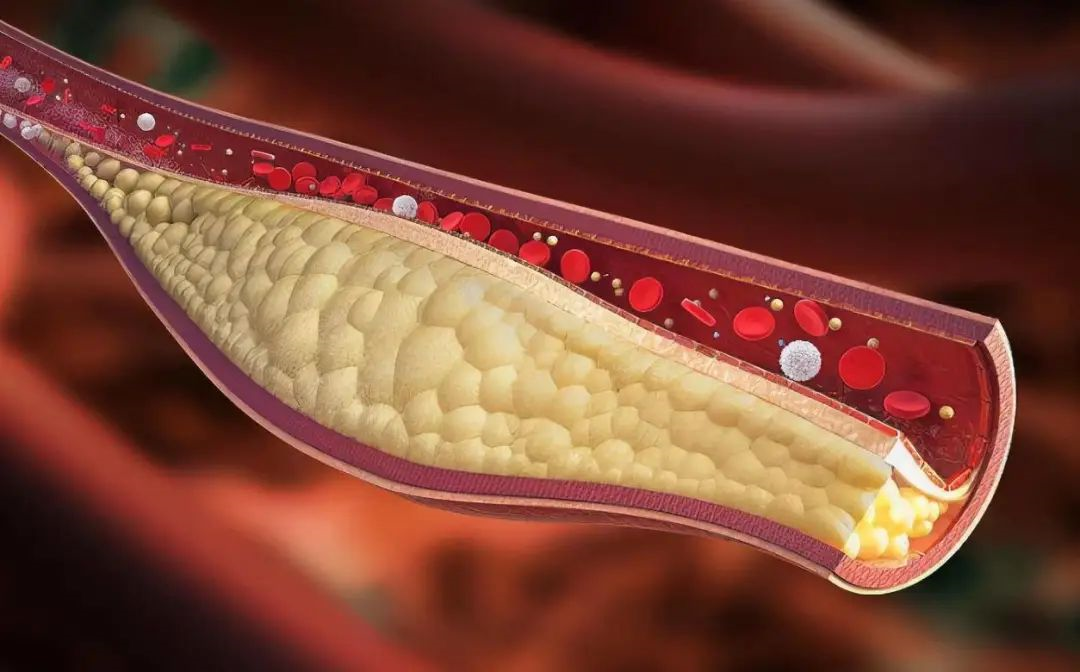
Studies show that natural astaxanthin can also reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, improve blood lipid profiles, promote improved blood flow in capillaries, and lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension.
Astaxantina can relieve heart failure caused by high blood pressure
Once the blood vessels harden, the viscous substances accumulated on the blood vessel walls over the years will prevent the blood vessels from relaxing, causing the heart muscle pump to have to work hard to make the blood flow through the blood vessels, and the blood pressure will rise accordingly. Overwork may also cause failure.
A Japanese study found that the blood pressure of hypertensive rats supplemented with astaxanthin for 2 weeks significantly decreased; stroke-prone rats supplemented with astaxanthin for 5 weeks had delayed onset of stroke and lowered blood pressure. Astaxanthin can reduce the elastic band of the aorta (the viscous tissue that causes arterial stiffness, or arteriosclerosis) and reduce the thickness of the arterial wall, helping to soften and prevent blood vessels from “hardening” (Hussein, 2005, 2006).
Astaxantina May Reduce Heart Attacks
An interesting animal experiment showed that after animals with heart disease or myocardial damage were given natural astaxanthin, their heart muscle damage or dysfunction was significantly improved. The researchers concluded that astaxanthin could help counteract the damaging effects of oxidants produced by oxygen-starved tissue during a heart attack. (Lauver, 2005; Curec, 2010).
In experiments with human volunteers, participants who supplemented with 6 mg of natural astaxanthin daily showed significant improvements in their blood flow after just 10 days of supplementation. (Miyawaki,2008)
Astaxanthin reduces inflammatory markers of cardiovascular disease
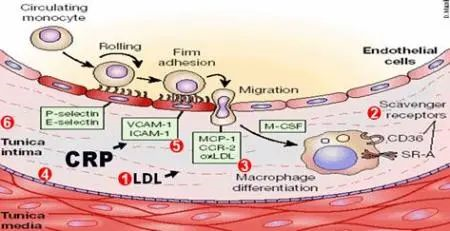
Research shows that astaxanthin can reduce blood levels of CRP (C-reactive protein). CRP is a biochemical that rises when there is excessive inflammation in the body. Elevated CRP is a marker measured when a person is suffering from cardiovascular disease. (Spiller,2006)
Astaxanthin can effectively improve blood lipids
When healthy blood fats like cholesterol become “oxidized”, they become bad cholesterol and stick to tissues (such as the lining of blood vessels). Research shows that astaxanthin can reduce the fats that cause artery clogging (such as oxidized low-density lipoprotein and triglycerides), increase the fats that clear the arteries (such as high-density lipoprotein), and reduce the ability of LDL cholesterol to be oxidized. (Awamoto, 2000)
() ()