Materia prima cosmética con efecto blanqueador--Arbutina

¿Qué es la arbutina
Arbutin, also known as arbutin, has a chemical name of 4-hydroxyphenyl-D-glucopyranoside and a relative molecular mass of 272.25. It is a naturally occurring glycoside derived from green plants and is an ingredient in many resistant Freeze-dried plants, such as wheat, pears, and bearberries of the Rhododendron family, are rich in solutes. They appear as white needle-shaped crystals or powders. They are easily soluble in hot water, methanol, ethanol, propylene glycol, and glycerin, and are insoluble in ether, chloroform, and petroleum. Solvents such as ether.
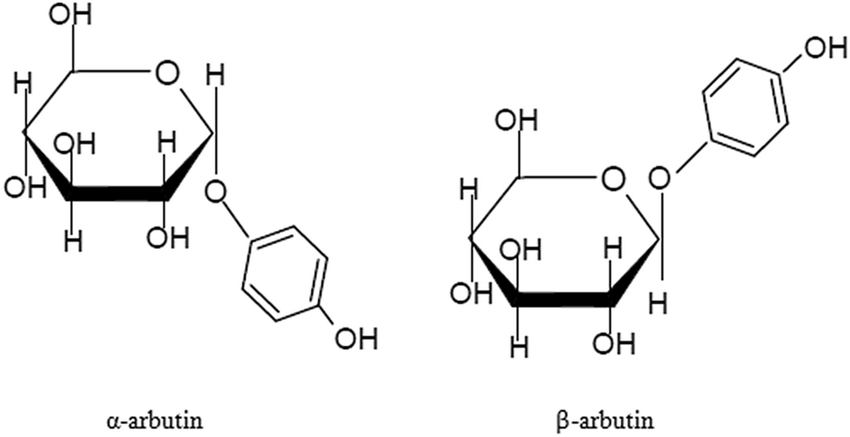
Arbutina can be divided into α-type and β-type according to different structures. The chemical name of α-arbutin is 4-hydroxyphenyl-α-D-glucopyranoside, and the chemical name of β-arbutin is 4-hydroxyphenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside. α-Arbutin is the epimer of β-arbutin, and the direction of its glycosidic bond in space is opposite to that of β-arbutin (see figure for details)
The whitening mechanism of arbutin
El contenido y la distribución de la melanina son los principales factores que determinan la profundidad del color de la piel. La melanina se produce en los melanocitos de la capa basal de la epidermis cutánea. Finalmente se forma a partir de la tirosina bajo la acción de la tirosinasa a través de una serie de complejas reacciones bioquímicas. Se transfiere de la capa basal a la capa externa de la epidermis de dentro hacia fuera a través de sinapsis. Colorea la piel.
La tirosinasa tiene actividad tirosina hidroxilasa (cataliza la tirosina para producir dopa) y actividad dopa oxidasa (cataliza la dopa para producir dopaquinona). En el proceso de formación de la melanina, es la principal enzima limitante. Su actividad determina la cantidad de melanina que se forma.
La arbutina es un inhibidor de la tirosinasa que puede inhibir eficazmente la actividad de la tirosinasa sin afectar a la concentración de proliferación celular. Compite por la unión de la dopa a través de su unión directa a la tirosinasa. sitio, bloquea la síntesis de dopa y dopaquinona, interfiriendo así con los melanocitos e inhibiendo la producción de melanina. Al mismo tiempo, también tiene la función de diluir la melanina formada, acelerar la descomposición y excreción de melanina, reducir la pigmentación de la piel y eliminar manchas y pecas.
Preparation method of arbutina
natural plant extraction method
This method mainly uses plant leaves of the genus Ursi as raw materials, and uses organic solvent extraction, extraction, column chromatography and other separation and purification methods to obtain arbutin extract. As early as 1930, it was reported that arbutin is contained in the leaves of rock cabbage. Subsequent studies have confirmed that arbutin is also found in the leaves of black rice tree, bilberry, bearberry and pear tree. glycosides.
Since the content of arbutin in plants is very low, the extraction process is relatively complex, and the purity of the extract is not high, so with the development of other preparation methods, the plant extraction method has gradually lost its competitive advantage.
plant tissue culture
The plant tissue culture method utilizes the glycosylation ability of plant cells to convert hydroquinone into arbutin. Compared with plant extraction methods, the efficiency of obtaining arbutin using plant tissue culture methods is much higher. When applying this method, selecting an efficient plant tissue culture medium and determining appropriate culture conditions are key.
The raw materials used in the plant tissue culture method are clean, the conversion rate is high, and the production is pollution-free. However, the production cycle is long, the separation and purification is complicated, and the industrial development is relatively immature. Further understanding the growth mechanism of plant cells, clarifying the key influencing factors of the synthesis process, shortening the production cycle, and improving yield are the key issues that need to be solved in the application of this method.
enzyme synthesis method
The enzyme synthesis method mainly uses glycosyltransferase or glycosidase as a catalyst to catalyze glycosyl transfer and reverse hydrolysis reactions to synthesize glycosides, that is, arbutin is obtained from hydroquinone and glucose under the catalysis of glycosidase.
The enzyme synthesis method has a simple process, high synthesis efficiency, and very optimistic development prospects. With in-depth research on this method in recent years, more and more suitable zymogens have been discovered, and the synthesis rate of arbutin is also getting higher and higher. It is believed that this method will be one of the main research directions for the synthesis of arbutin in the future. one.
chemical synthesis
Generally, chemical synthesis of arbutin uses glucose and hydroquinone as raw materials. After the two are appropriately protected, they undergo a glycosidation reaction and then remove the protecting group. The chemical synthesis method has become the most important method for preparing arbutin due to its advantages of better synthetic product quality and lower production cost, and has achieved industrial production at home and abroad.
At present, in China, anhydrous glucose is generally used as raw material, and β-arbutin is produced through acylation protection, catalytic condensation, and alkaline hydrolysis. With the continuous development of synthesis technology, in recent years, the steps for domestic synthesis of arbutin have been gradually simplified, the synthesis rate has been continuously improved, and the quality has reached the international advanced level. However, due to the poor stereoselectivity of the product in chemical synthesis, more in-depth research is still needed to find an efficient and specific chemical synthesis method for preparing α-arbutin.
() ()